The most basic tuning method for a magnetic loop antenna involves adjusting the capacitor until the noise level, which is the background static or interference picked up by the antenna, reaches its peak. This indicates that the antenna is resonating at the desired frequency.
Another more precise method is to transmit at the desired frequency and adjust the capacitor position until the Standing Wave Ratio (SWR) is at its minimum.
While both of these methods require manual adjustment, the following approach takes antenna tuning to the next level with an automated solution.
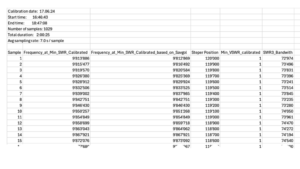
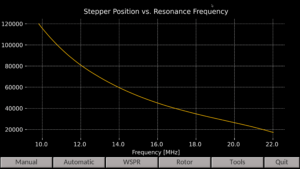
By integrating a sophisticated polynomial model derived from real-world Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) sweeps, the control system predicts and adjusts the optimal capacitor position with exceptional accuracy within a very short time.
This automated method not only enhances tuning precision but also reduces the time required to achieve optimal antenna performance.
The Python application on the Raspberry Pi calculates precise adjustments based on the desired operating frequency, ensuring the antenna operates efficiently without the need for manual fine-tuning.
The technicalities of the polynomial models utilized are complex, but it can be thought of as having a table that provides stepper motor positions corresponding to desired frequencies